
If the wave has normal incidence, then its reflection coefficient can be expressed as: V2 velocity of medium 2. Application for drawing standing wave diagrams including the reflection coefficient, input impedance, SWR, etc.Ψ ( s + 1 ) = − γ + ∑ k = 1 ∞ ( 1 k − 1 k + s ) \psi(s+1)=-\gamma+\sum_. Geophysics The ratio of amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave, or how much energy is reflected.Flash tutorial for understanding reflection A flash program that shows how a reflected wave is generated, the reflection coefficient and VSWR.Where ns is a specular reflection parameter. This model sets the intensity of specular reflection directly proportional to the cosns(). Wikimedia Commons has media related to Smith charts. We are going to prove the reflection formula 7T r(s)(1 - 8) sin(8) By substituting the definition of the gamma function, this becomes r-e-de de yu+)-. An empirical model for calculating the specular reflection range, invented by the Phong Bui Tuong is also known as Phong specular reflection model.

Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document: "Federal Standard 1037C". Reflections of signals on conducting lines. It is most often measured at the transmitter side of a transmission line, but having, as explained, the same value as would be measured at the antenna (load) itself.Īcousticians use reflection coefficients to understand the effect of different materials on their acoustic environments. The ray of light hitting the surface is called the incident ray. While having a one-to-one correspondence with reflection coefficient, SWR is the most commonly used figure of merit in describing the mismatch affecting a radio antenna or antenna system. Reflection is when light bounces off the surface of an object, and all reflected light obeys the law of reflection. In terms of the forward and reflected waves determined by the voltage and current, the reflection coefficient is defined as the complex ratio of the voltage of the reflected wave ( V −. Formula, Examples, Practice and Interactive Applet on common types of reflections like x-axis, y-axis and lines: Reflections: Interactive Activity and examples. The reference impedance used is typically the characteristic impedance of a transmission line that's involved, but one can speak of reflection coefficient without any actual transmission line being present. The voltage and current at any point along a transmission line can always be resolved into forward and reflected traveling waves given a specified reference impedance Z 0. Determination of NHZ from the reflection of a laser: Given a 250 mW visible CW laser with a divergence of 1mrad and an incident surface spectral reflectance of 0.2, determine the range that a reflected beam is equal to the MPE. Corresponding parts of the figures are the same distance from the line of reflection. For conservative calculation, you may use the NOHD formula for a specular reflection. To perform a geometry reflection, a line of reflection is needed the resulting orientation of the two figures are opposite. In telecommunications and transmission line theory, the reflection coefficient is the ratio of the complex amplitude of the reflected wave to that of the incident wave. Geometry Reflection A reflection is an isometry, which means the original and image are congruent, that can be described as a flip. 
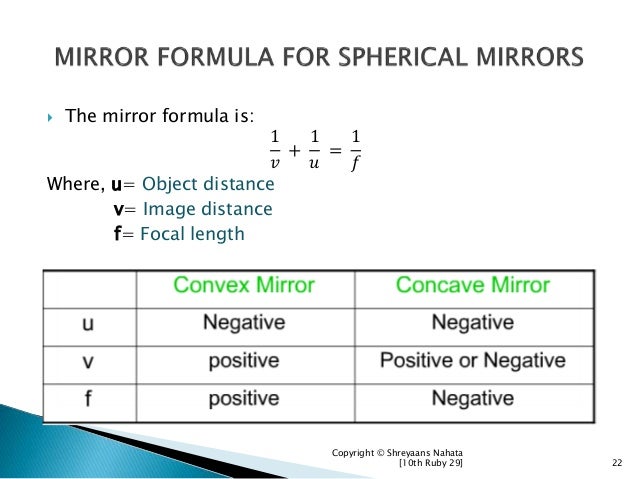
See also: Reflections of signals on conducting lines and Signal reflection Formula 1 o 1 i + 1 f 1 object distance 1 image distance + 1 focal length Magnification (M) It is the increase (or decrease) in the size of an image produced by an optical system compared to the true size.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
